Imagine traversing through another world where physical limitations are not restrained, where we can see our imagination with our own eyes. Envision stepping inside a beloved video game, a cult classic or one of your own creation, and becoming the main character.
Could we be the next stars of the games we love to play?
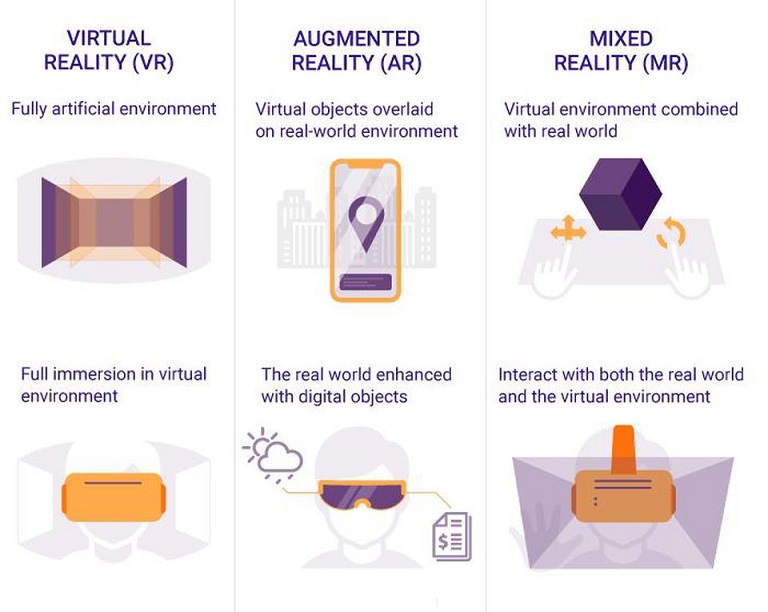
You’ve likely heard of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), but have you heard of Holographic Augmented Reality (Holographic AR)? Hologracphic AR is the next generation of AR.
 Let’s start with a simple definition:
Let’s start with a simple definition:
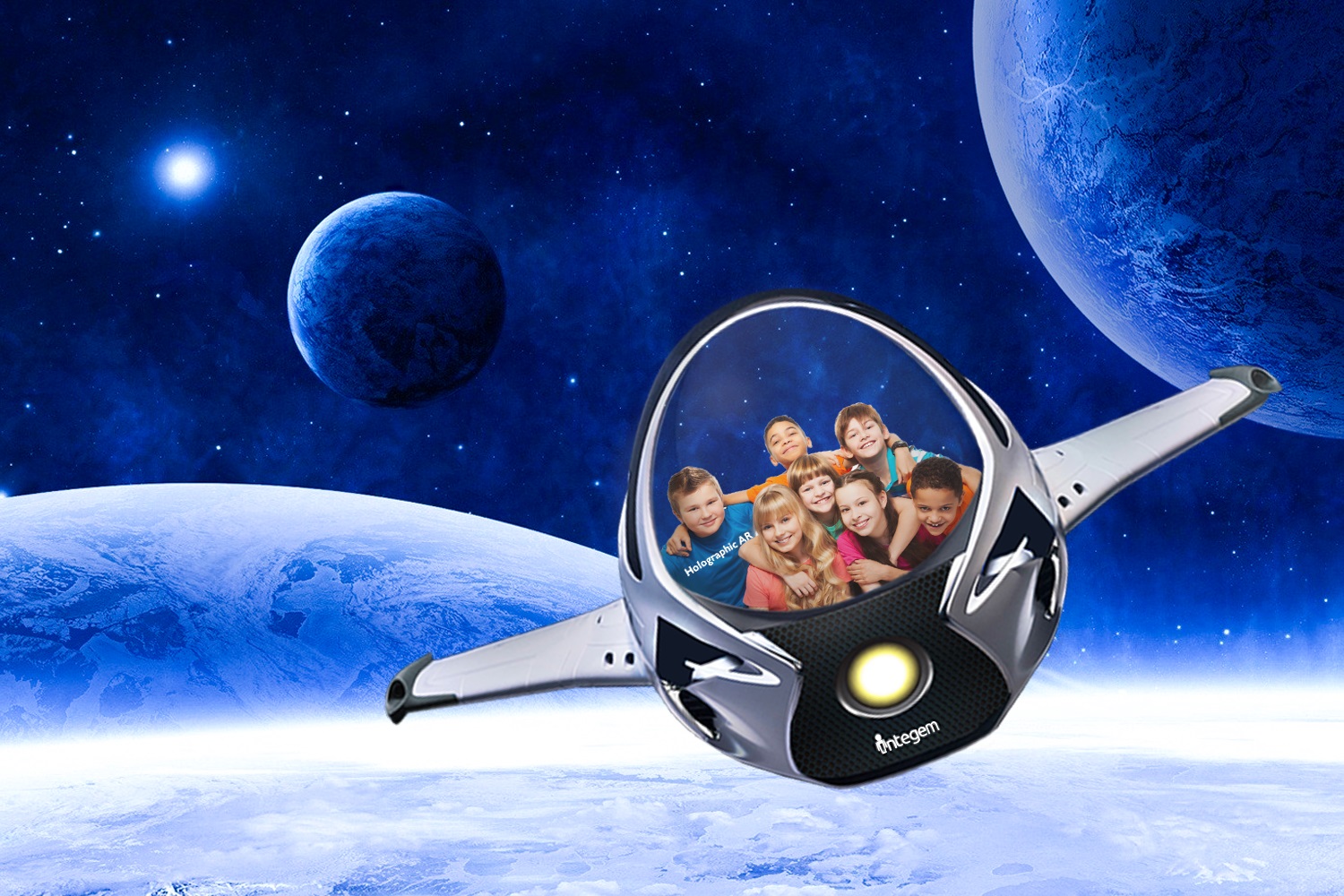
Holographic Augmented Reality extracts people and/or objects from the real world, in real time, and immerse them into the virtual environment where they can interact with digital elements naturally. In other words, Holographic AR allows users to see themselves in the virtual world and interact with objects found within the same space.
Similar to Augmented Reality, Holographic AR can overlay digital objects in a real-life scene. In place of the traditional saying “seeing in believing”, Holographic AR empowers people to see themselves in any world they wish to see, like being on Mars or at the bottom of the ocean. In contrast to the traditional use of Human Computer Interaction (HCI), like the use of a keyboard or touch screen as controls, Holographic AR uses a natural user interface (NUI), where specific body movements, hand gestures, facial expressions, and voice commands have sequential responses and outcomes.
To understand what Holographic Augmented Reality is, it first helps to provide some perspective to the different types of realities that make up immersive technology. By clarifying terms that are often confused with Holographic AR, like Virtual and Augmented Reality, we can begin to truly understand the capabilities Holographic AR holds to us.
[Source: Forbes]
Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality, often shortened to VR, encompasses the experience of interacting within a completely computer-generated world. By emphasizing and incorporating visual and auditory sensory feedback, this provides users with a highly in-depth, immersive ‘new world’ they can explore, perform actions and see/experience the response.

[Source: Wall Street Journal ]
VR utilizes a headset that partially covers a person’s face, from the forehead to the bridge of the nose, and a set of controls for each hand that allow the user to move, grasp, and act within the virtual space. While users are experiencing VR and effectively discovering a new space, they are essentially blind to their own real-world environment. Following safety guidelines, like interacting with the system in a clear, open space to having another person monitor safety, allows the user to become fully immersed into the digitized space without worrying about possible injury in the real world.

[Source: Business Computing World]
VR software and hardware has been industrialized by a vast variety of developers, from big companies like Google to smaller, independent makers creating free applications. VR products like the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive, developed respectively by Oculus and HTC, provide users with a highly immersive interface, sleek design, and many applications to choose from, a majority of which are free to use. While these products are on the higher end of price and availability, they provide users with cutting-edge technology and memorable experiences to both captivate and expand their knowledge in immersive reality.

On the other side of the spectrum, more immersive reality products often utilize smart phones like the iPhone and Android to run VR applications, often free to use, which in turn provide mobile users with a similar experience at a more affordable and accessible rate. Such applications like Google Earth VR (combined with the Google Cardboard, a makeshift, low-cost headset) provide the similar VR experience to a larger audience. This has especially been useful for introducing VR and comparable immersive technology to young kids and students in the classroom to teach them about the environment and insight into different countries and cultures.

[Source: Tech Trends]
Virtual Reality has pioneered innovative minds to push the boundaries of what is real and what is imagined. Whether it is to provide entertainment or a new learning experience, VR provides all age groups a chance to learn, expand, and problem solve. By having a multitude of creators design and develop new realms to explore, the fascination surrounding VR’s innovative streaks can only continue to wow everyone.
Augmented Reality (also called first generation AR)
Augmented Reality, often shortened to AR, encompasses the experience of interacting in the real-world environment with digital elements overlaid and “augmented” within the same space. Where VR completely replaces the real world with a new one, AR alters the user’s perception of the physical environment in real time. It provides similar sensory feedback, like visual and auditory, and can introduce others like hap-tic (grasping/pinching motion) to better view and move about the hybrid space.
 Unlike VR, AR does not generally utilize a headset or controllers. Rather, the user views the hybrid world through a screen, often from a smartphone or tablet, and can move about freely and safely without their eyes or bodies blinded and subjected to injury. Often, AR applications utilize the user’s hands to act as the controllers, mainly through finger touching and pinching of the screen to zoom in/out, turning, and grasping/pulling digital objects.
Unlike VR, AR does not generally utilize a headset or controllers. Rather, the user views the hybrid world through a screen, often from a smartphone or tablet, and can move about freely and safely without their eyes or bodies blinded and subjected to injury. Often, AR applications utilize the user’s hands to act as the controllers, mainly through finger touching and pinching of the screen to zoom in/out, turning, and grasping/pulling digital objects.
Pokémon GO has become one of the biggest, most widely used AR applications since 2016. It catered to many die-hard fans’ wishes by creating the ability to physically explore the real world that mirrors the Pokémon world, along with giving them the power to catch Pokémon seen through screens, as if they were physically in the real world. The use of AR in this setting brought a cult classic as close to life as it could possibly get. Moreover, another popular mobile application that garnered major attention was Snapchat, which used AR capabilities to augment a person’s appearance via facial filters. People could see themselves morphing into different animals, scary creatures, or even “swapping” faces with another user on screen. By capturing users’ facial features, digital elements overlay and distort the image on screen in a variety of ways.
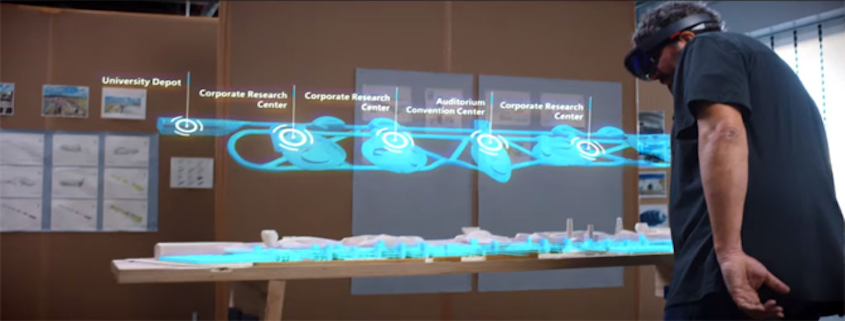
While most AR applications do not utilize a headset, there are some AR products that do use a smaller set eyewear to provide a more in-depth interactive experience without completely blinding the user from the real world. Products, like the Microsoft Hololens to Magic Leap’s anticipated Magic Leap One, requires the use of AR glasses/gauges to see overlaid digital objects in the real world and provides users with a private view of the virtual world.

Tech giants like Apple and Google, have both announced more support for AR development in mobile devices while smaller, independent developers are looking to integrate AR capabilities more into societal needs, like helping people with map directions, creating interactive tours of landmarks, and letting the public learn new concepts. Whilst AR applications still have their limits, like having too small of a screen or inconvenient movement issues for public use, Augmented Reality is still steadily picking up pace in every corner of the technology landscape.
So what is Holographic Augmented Reality (also called next generation AR)?
Holographic Augmented Reality, abbreviated as Holographic AR, encompasses the experience of extracting people and/or objects (their image) from real-life in real time and immerse them into the virtual environment to interact with digital elements naturally. By overlaying the person’s image into the digital interface, it makes it appear as if the user is in a completely different world.
An innovative aspect of Holographic AR is the use of body movement, like hand gestures, facial expressions, and voice commands, to act as the controllers of the experience. Rather than use controllers or other various devices, simple body movement feels more natural and is often linked to what is commonly referred to as Natural User Interface (NUI).
But what makes this interface “natural” when compared to other devices?

If you are someone that commonly uses their smart phone or laptop, while it may feel natural now, you may recall the learning curve of sufficiently getting accustomed to your device and how much time it took. This is referred to Human-Computer Interaction (HCI).
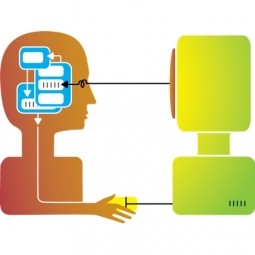
HCI consists of design and the implementation of interactive computing systems that people can interact with; this includes desktops, keyboards, smartphones, etc. The most important concepts of HCI are functionality and usability, and the success of technology is the result of how easy the user can interact with a device. Therefore, if the interface is hard to use or understand, people will likely not want to use the product and will ignore it in a majority of cases. So when it comes to new and emerging technology, especially with Holographic AR, VR, and AR, that is the most important aspect to keep in mind: having a system that is easy to use.
[Source: IoT One]
Natural User Interface (NUI) is a user interface that is effectively invisible while the user continuously learns more complex interactions with their body movements as controls. Machines and various software hold the capability of learning specific gestures and movements in order to provide a continuously personalized experience. The success of Holographic AR heavily relies on the ability to develop NUI technology that allows users to freely interact within the virtual environment.
The Benefits of Holographic AR
Cognitive Impact:
There have been a handful of professors and researchers leading studies to see the effects immersive technology has on the human mind and society at large. Jeremy Bailenson, the founding director of Stanford University’s Virtual Human Interaction Lab, studies the psychology of Virtual and Augmented Reality, particularly how virtual experiences lead to changes with self perceptions and of others. He builds and studies systems that allow people to meet within a virtual space and allows them to explore the changes of this type of social interaction. Recently, he has focused on transforming education, empathy, and health through virtual experiences.
Another study Bailenson took part in, with colleague Segovia, that used virtual avatars to determine the perceived volition of the user’s identity created in a manipulated state. This study further focused on one’s self perception and how immersive technology may or may not alter that. This study was featured in The Social Net, edited by Yair Amichai-Hamburger; the main focus of the book was to understand online behavior at the psychological level.
Early Childhood Development:
Early childhood education emphasizes learning through experience and practice. When it comes to Language/Speaking Development, early literacy depends greatly upon high-quality experience that stimulate listening and speaking. The most efficient way to build up vocabulary and awareness of sentence structure is through real-world experiences. Child educators globally offer enriching, stimulating provision to their students every day – and Holographic AR just gives them an additional immersive tool.
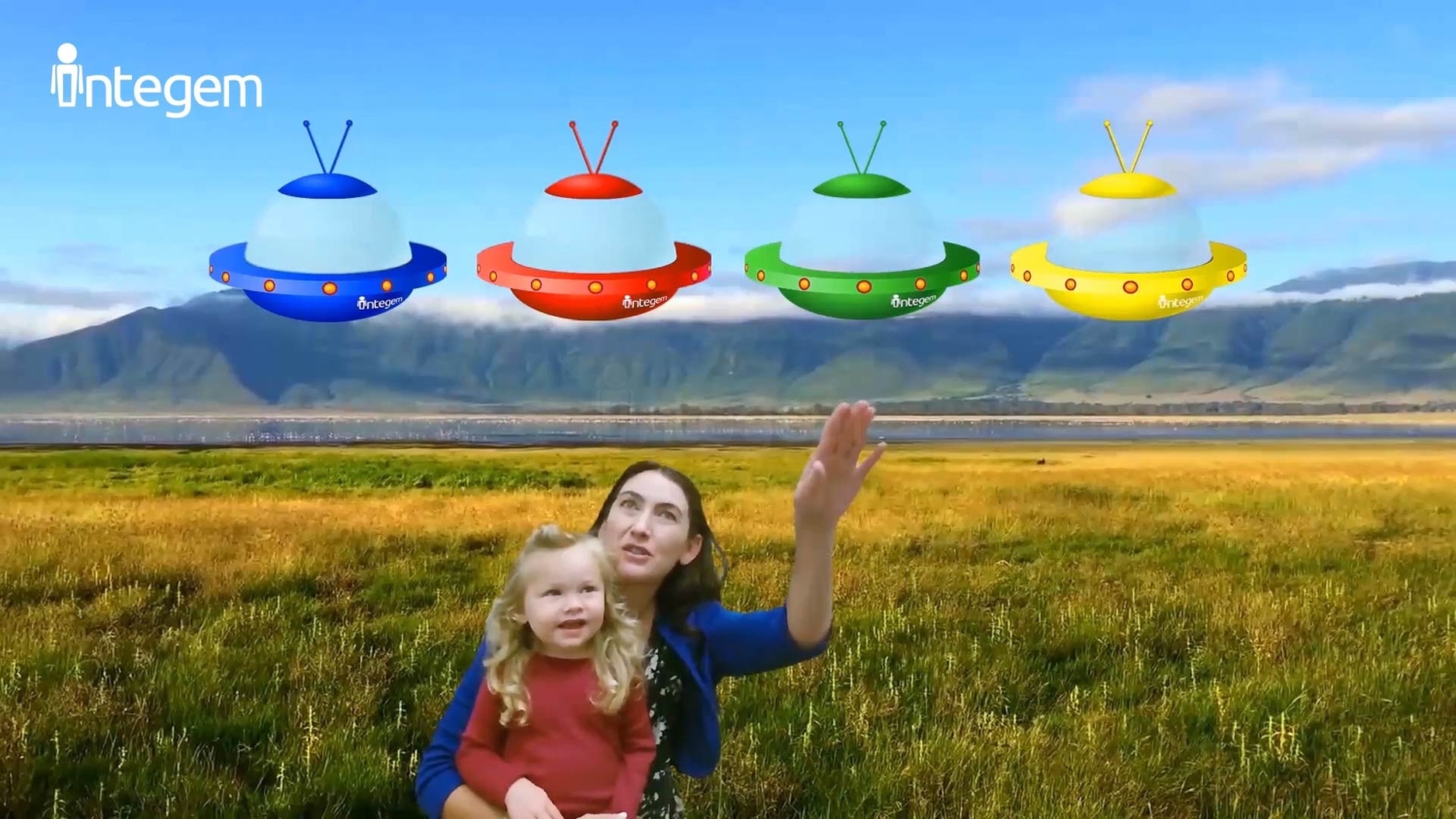

Enhancing real-life experiences
Like taking young children on field trips to the park or a museum, is an effective way to teach them about the world. But even after the field trip is over and the memories slowly fades from them, Holographic AR allows kids to re-live the experience and excitement through virtual simulation and offers the greater potential to further extend their comprehension.
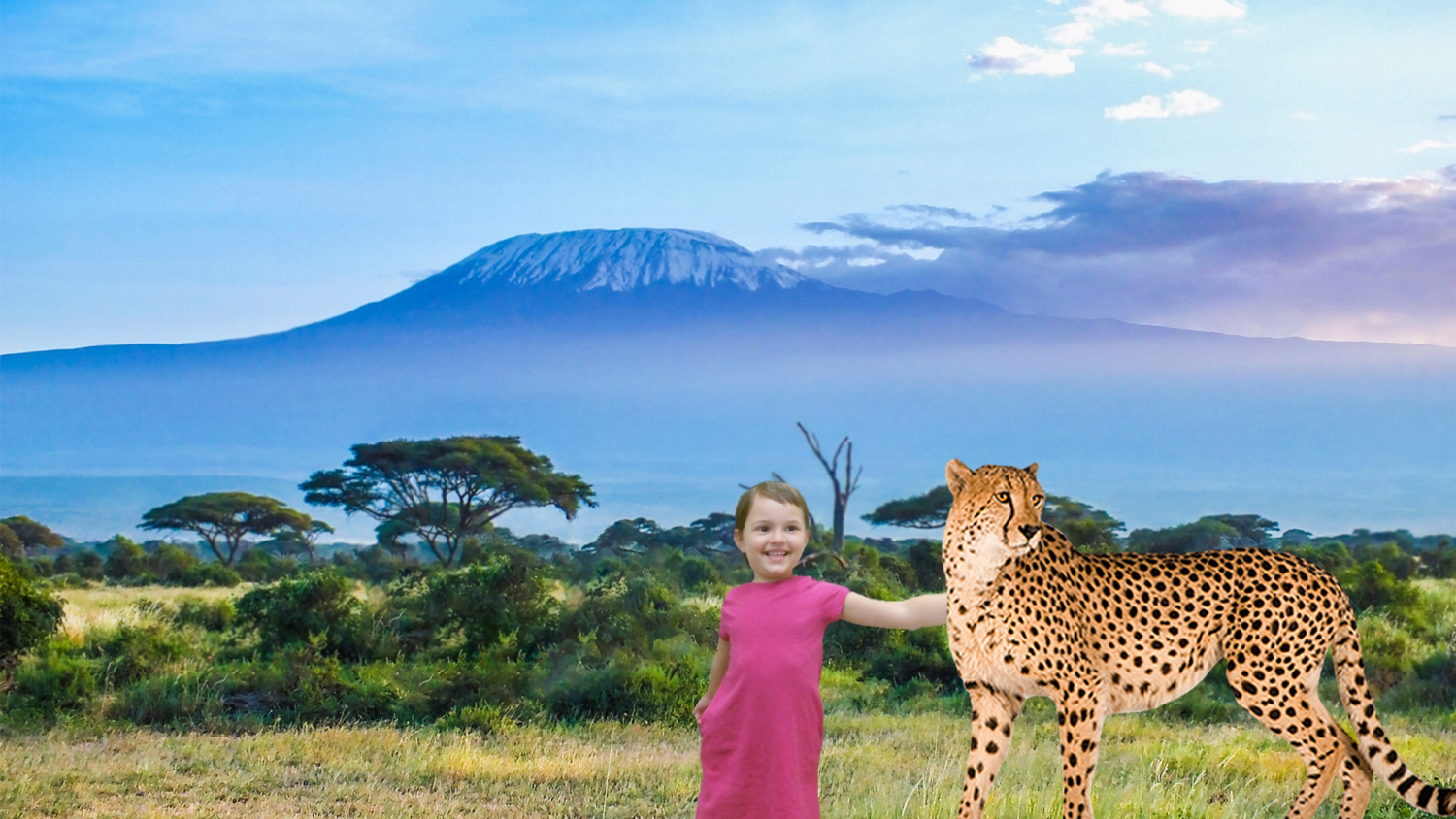

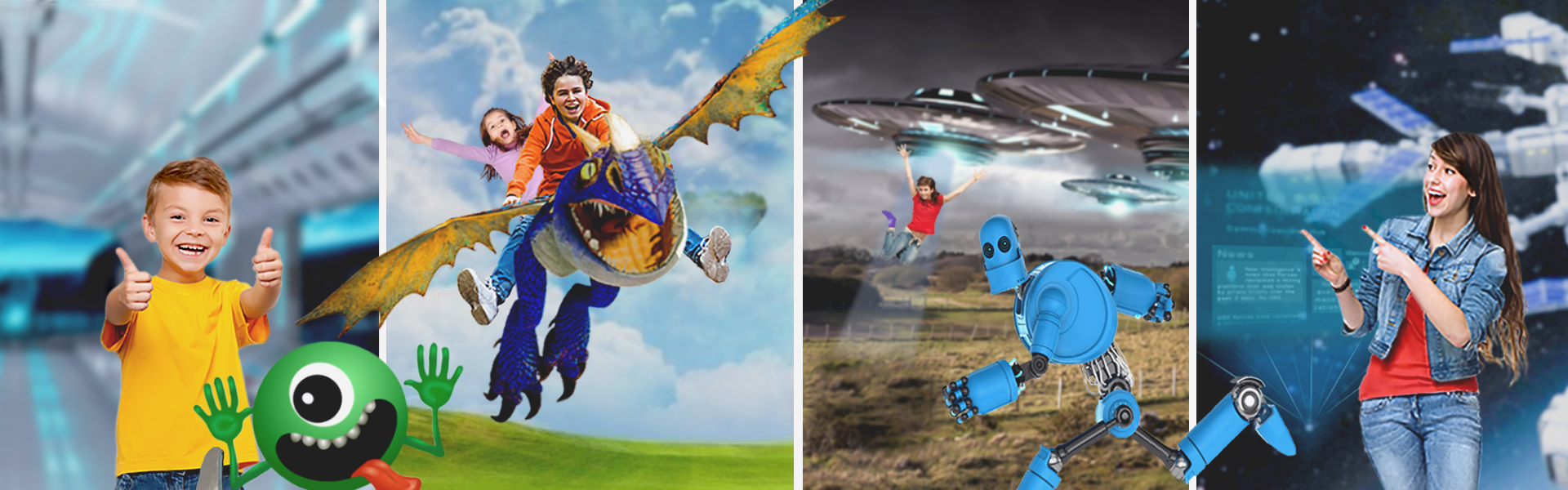
But even before taking field trips or traveling to a different area, to understand or discuss something you have never witnessed with your own eyes can be extremely difficult. For example, many children may not have yet experienced visiting the city or gone to see the ocean. With Holographic AR, it opens the mind for imagination and opportunities and allows kids to see and experience something they have not yet done or may find a realistic difficulty in doing. For example, a little girl who loves butterflies gets the opportunity to see herself as a butterfly! It fosters the imagination and better prepares them for future experiences.
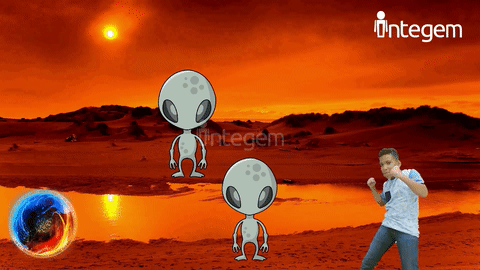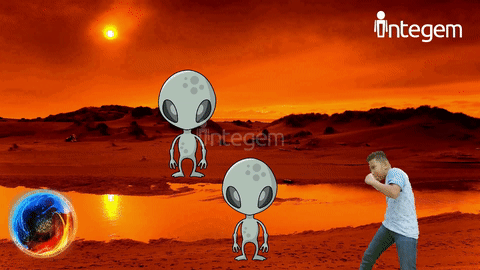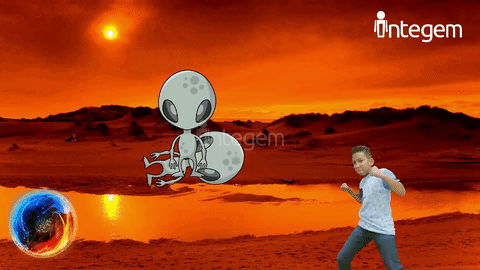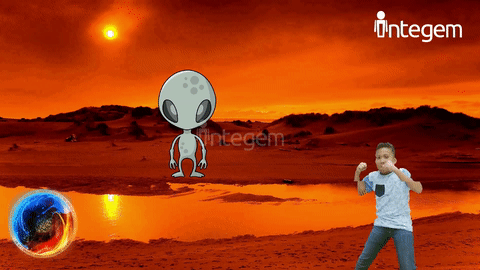
Reducing Cognitive Load:
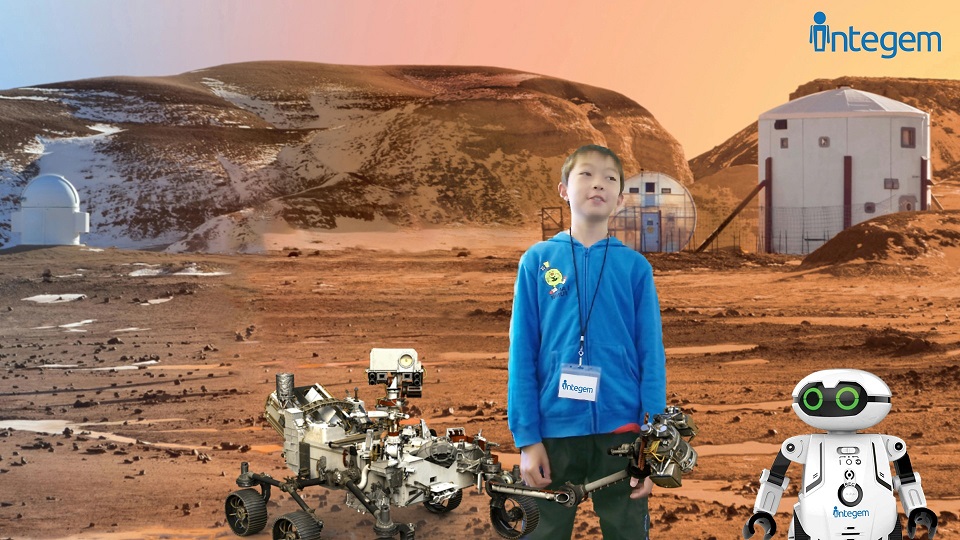

It is important to better comprehend AR parameters and impact on user performance as immersive technologies become increasingly popular and more commercially available. Studies have shown an increase in user performance and reduced cognitive load when certain tasks are presented using AR. In one experiment, researchers compared AR to a handheld device to follow map directions of a college campus versus using Google Maps on a smartphone. The results found that students using the AR application had lower cognitive load and a higher situational awareness than those that used Google Maps. The answer was straight-forward: it was easier to simply have directions floating in a visual field and overlaid onto the physical environment. This results in reducing cognitive load by eliminating the need to shift attention back and forth from the phone to the surrounding physical area.
Business Applications:
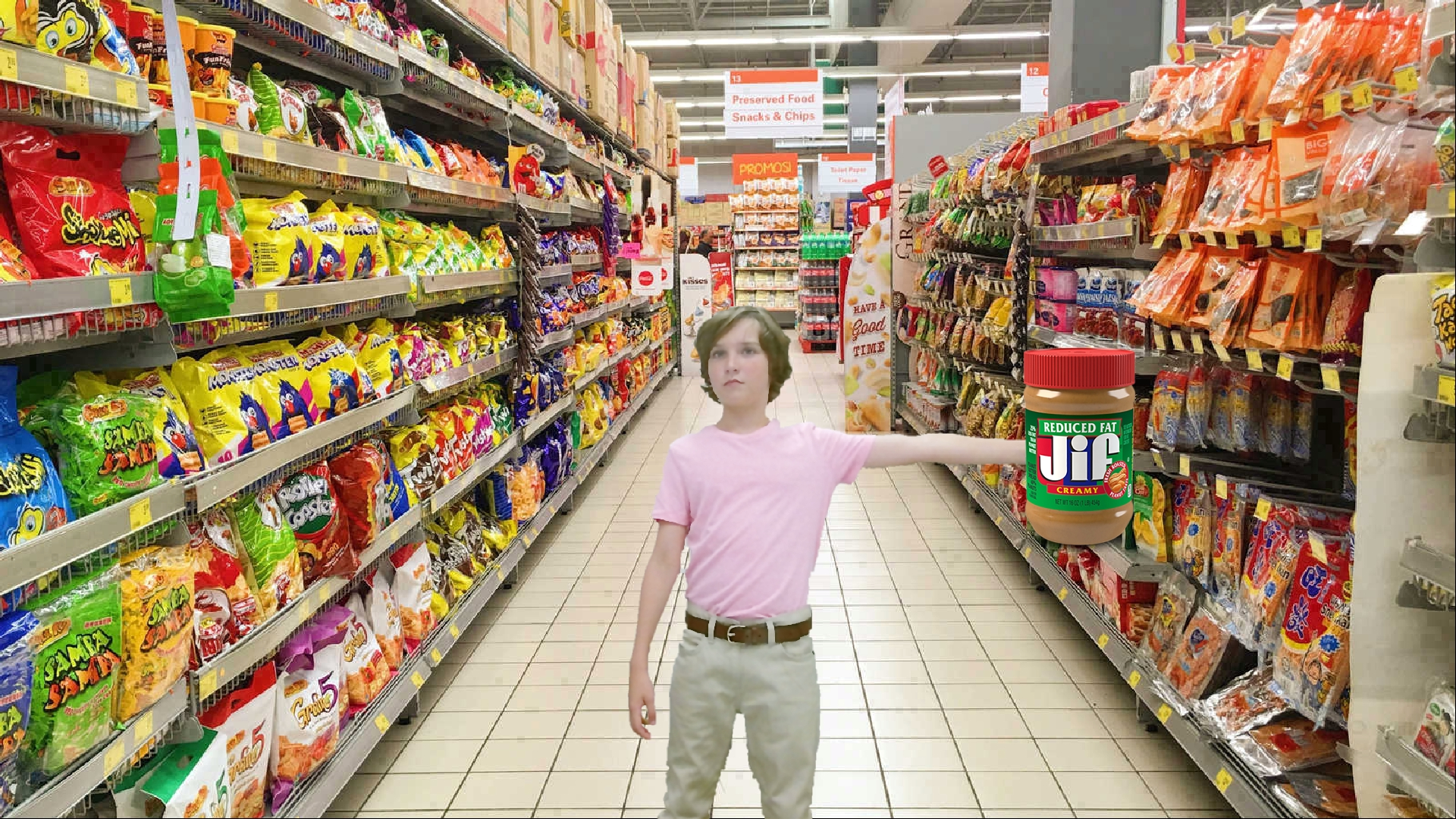

It is simple to see why audiences have been captivated by immersive technology’s ability to blend reality with non-reality. Customer visualize how different products can become part of their daily life, which is why it is such a natural fit for product experiencing, presentation, and marketing/advertising. It provides a whole new level of on-line shopping experience.
For businesses and Retail, Holographic AR empowers companies to create their own personalized experiences to provide customers with a one-of-a-kind application and give employees on the floor another creative outlet to express their knowledge and enthusiasm.
The Future of Holographic Augmented Reality
So what does the future of Holographic AR have in future for us?
It does and continues to evolve interactive entertainment for families and friends alike. It will assist problems found within the classroom and provide students with an education not only defined by reading textbooks or by watching informational videos. Advertising can be a fun, more personalized experience where brands and consumers have a medium to interact in.
The possibilities are looking endless as long as innovation and imagination of bright minds lead the way. The evolution of interactive technology has captivated the majority of all audiences that have followed and kept up with innovative breakthroughs both in software and hardware. Interactive and immersive reality was the head-turning key word that promised excitement and delivered innovation.
Where to Learn Holographic AR Now?
You can send you kids (K-12) to Integem Holographic AR Summer Camp. The camp provides a great learning environment and experience to students. With 8 students per instructor, students will get individual attention. Through hands-on projects, campers will create their own Holographic AR outer-space/nature adventures; Holographic AR animated comics; Holographic AR Broadcasting studio; and/or interactive 3D Holographic AR movies/games. Campers will learn STEM/STEAM concepts, computer animation, UX/UI Design, 3D modeling, artificial intelligence(AI), and visual communication. Suitable for ages 6-18 of all computer skills, from zero experience to advanced levels. Learn more at camp.integem.com.







Recent Comments